15. Integration Testing
Integration and Functional Testing
ND079 JPND C3 L5 A10 Integration And Functional Testing V3
Automated Testing Scope
- Unit Tests: Easiest to write and maintain, narrowest scope. Write the most of these.
- Integration Tests: Test the interaction between Units. Span multiple components.
- Functional Tests: Verify the behavior of your application from start to finish, including interaction with the UI and database.
Integration Testing
ND079 JPND C3 L5 A11a Integration Testing V2
Common Integration Test Targets
- Database
- External APIs
Testing Databases
Use In-Memory Databases
- H2 database
- Hibernate can automatically construct database from your class definitions.
- Otherwise, you can use a SQL script that constructs the test database.
Interacting with Test Databases
- Basic Solution: Connect in @BeforeAll
- Spring Framework: Separate config file for tests
- Test Frameworks to Populate Test Databases: Unitils
Database Interaction and unit tests covered in greater detail in the Java Web Developer Nanodegree
Testing External APIs
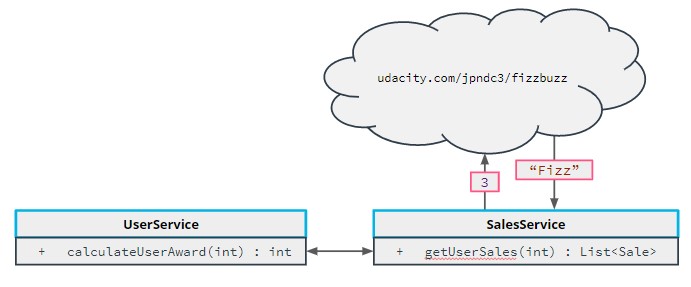
External API Integration Test
ND079 JPND C3 L5 A11b WireMock Demo
WireMock
WireMock is a tool that allows you to programmatically create fake HTTP endpoints for external API integration testing.
This is an example class that connects to an external API to retrieve the value of fizzBuzz:
public class ExternalSalesService implements SalesService {
private String resource;
public ExternalSalesService(String resource) {
this.resource = resource;
}
@Override
public String fizzBuzz(int i) {
//send a request to url/fizzbuzz/{i}
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder(URI.create(resource + i)).GET().build();
try {
HttpResponse<String> response = HttpClient.newHttpClient()
.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
return response.body();
} catch (InterruptedException | IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error retrieving value for " + i, e);
}
}
}Writing an integration test that uses this class requires a valid http endpoint for it to use. Wiremock allows us to create that endpoint.
class ExternalSalesServiceTest {
static WireMockServer wireMock = new WireMockServer(wireMockConfig().port(8089));
private static String serverPath = "http://localhost:8089";
private static String fizzBuzzPath = "/fizzbuzz/";
ExternalSalesService fizzBuzzService;
@BeforeAll
static void setup() {
wireMock.start();
}
@AfterAll
static void cleanup() {
wireMock.stop();
}
@BeforeEach
void init() {
wireMock.resetAll();
fizzBuzzService = new ExternalSalesService(serverPath + fizzBuzzPath);
}
@Test
public void externalFizzBuzz_passedValue_returnsExternalResponse() {
int i = 3;
String expected = "Fizz";
wireMock.stubFor(get(urlEqualTo(fizzBuzzPath + i))
.willReturn(aResponse().withStatus(200).withBody(expected)));
String response = fizzBuzzService.fizzBuzz(i);
assertEquals(expected, response);
}
}